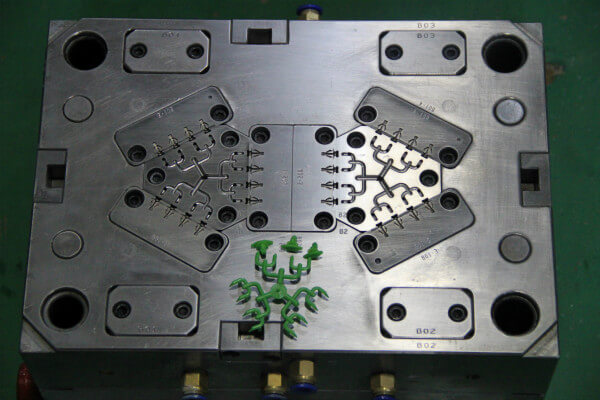
M OLD STRUCTURE:
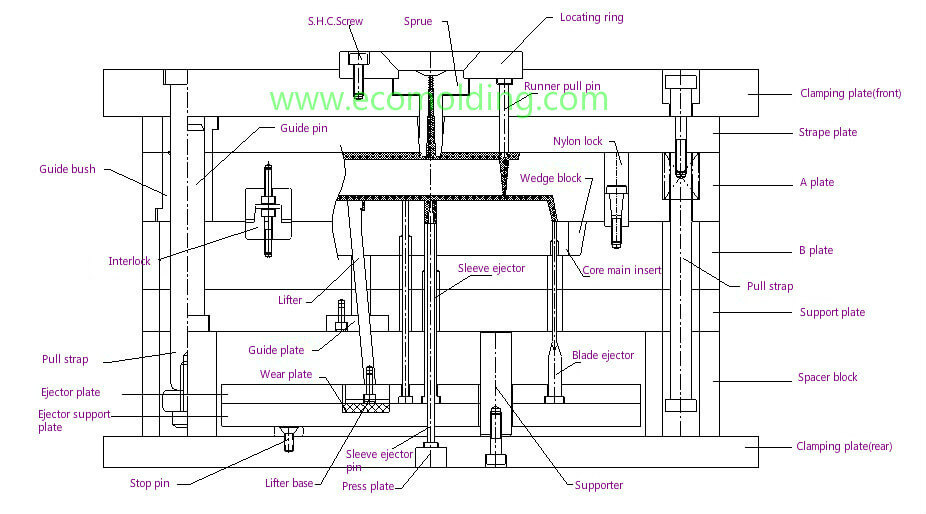
The seven systems of injection mold: Gating system, guidance system, molding system, core pulling system, ejection system, cooling system, and venting system.
- Gating System:
Runner: Where the molten plastic flows through before reaching different cavities.
Sprue: Where the molten plastic flows through from the injection machine to the mold.
Gate: The last opening that allows the molten plastic to flow into the cavities.
Cold Slug Well: When the molten plastic flows in the sprue and runner, it will solidify due to heat transfer with the mold. The cold slug well is where the solidified material is stored before entering the cavities.
- Guidance System:
In-mold opening/closing process, mold displacement will occur due to manufacturing tolerances and installation tolerances. When the mold is closing, it is required that the mold can return to its original position. This is where guidance and location (i.e. mold guidance system) fit in.
- Molding System:
Molding System: A closed space that consists of the core, cavity, and inserts, etc.
- Ejection System:
The ejector of the injection machine applies force on the press plate of the mold, which drives the ejector pins, ejector blocks, and lifters, etc. to push the product away from the core or the cavity and thus enable smooth mold release.
- Cooling System:
The mold itself is a large cooling system. To achieve a better cooling effect, one or more groups of cooling channels will be designed for the mold. Usually, the distance between the cooling channel and the product is twice the diameter of the channel. The coolant is not necessarily cold water – it can be water at 100 degrees Celsius depending on the mold temperature and sometimes it can also be hot oil.
How to assemble a plastic injection mold?
P ROJECT MANAGEMENT:
Strong project management is our key to the success and quality of our products, All of our Project Engineers not only have significant experience in tooling and injection molding but are also fluent in English. The Project Engineers are responsible for the follow up of the tooling process, and for the timely reporting of the project's progress to the customer.
Our mission is to provide:
1, On-Time Delivery
2, An Assurance that our customer’s project is produced according to their order and standards
3, That communication is provided in a timely and clear manner
4, Complete project management and support from concept to final part inspection and approval.
M OLD STANARD:
Mold Steel: ASSAB(Sweden), DAIDO(Japan),FINKL(America),AUBERT & DUVAL(France), Thyssen(Germany), LKM (China)
Mold Base: EMP, DME, HASCO, FUTABA, LKM.
Hot Runner: MOULD MASTER, SYNVENTIVE, HASCO, DME, YUDO, INCOE
Standard Parts: DME, HASCO, LKM, HEB, STRACK, OPITZ
Texture: VDI 3400, Mold-tech, Yick Sang, Tanazawa, etc
Software: Pro/Engineer, Solidworks, AutoCAD, Moldflow, Unigraphics, CATIA, Mastercam
M OLD MAKING IN-HOUSE:
Our Mold shop is well equipped with latest machines, such as High-speed CNC machines, EDM wire cut machines, Mirror finish capable sinker EDM machines, They are all imported from Taiwan, Switzerland, and Japan. These machines help us to ensure the molds are manufactured to the highest precision with a quality finish. Moreover, all of our processes are in-house, which allows us to accomplish short lead times, Our shop has 30 skilled toolmakers, most of whom have more than 10 years of mold making experience, they are familiar with all machining processes, the costs of each step can troubleshoot during the mold building process. Our staff is vitally important to our company, Their experience, and hard work allow Eco molding to guarantee a high-quality mold at a reasonable price.




