The Runner Design Concept
- The runner refers to the melt flow passageway between the end of the main runner and the gate, which is used to change melt flow direction and allocate it to each cavity in a stable and balanced way.
- The basic design principle of the branch runner is little pressure/heat loss, with the minimum quantity of plastic retained in the runner.
- Sectional Shapes of the Branch Runner:
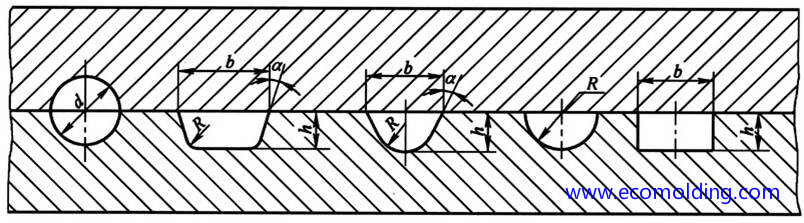
–Circular, with the minimum specific surface area (runner surface area/runner volume), but during production, both sides of the mold plate need to be aligned.
–The commonly applied forms, trapezoid and U-shape are easy to process.
–Semicircle.
–Rectangle, larger specific surface area and high resistance to flow, thus seldom applied.
The Principle of the Runner Design
- The runner is usually designed on either half of the plastic injection mold.
- When considering the layout of the cavity and the branch runner, it is better to ensure that when projected on the parting surface, the geometric center of the total projection area of the cavity and the runner overlap with the center of the clamping force.
- The internal surface roughness of the branch runner is 1.6. In this case, the outer layer melt flows faster than the inner layer melt inside the branch runner, which tends to cool down and thus form a heat insulation layer.
- The sectional size of the branch runner is dependent on the plastic part size/type, injection speed, as well as the length of the branch runner.
- Generally, when the diameter of a branch runner is smaller than 5 – 6mm, runner size will have a greater influence on fluidity; when the diameter is greater than 8mm, there will be little influence on fluidity.
- If the branch runner is very long, it might be better to further extend the branch runner along the flow direction to form a cold slug well, so that the cold materials will not enter the cavity.
- The branch runner cannot be too thin, or temperature/pressure loss will increase, which makes it hard to fill up the cavities far from the main runner.
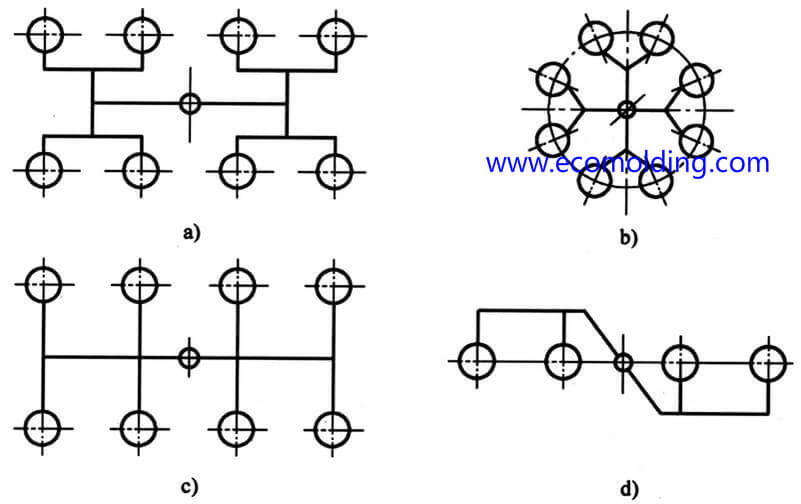
The Runner Design Layout
In a multi-cavity layout, it needs to be guaranteed that the molten plastic can concurrently fill up each cavity in a uniform way. There are 2 layouts, i.e. balanced and unbalanced:
Balanced: uniform filling, with each cavity concurrently filled.
Unbalanced: The runner is designed to be short to save raw materials.